Tel: +86-18874804206 E-mail: sales@innovequipment.com
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
- Home
- Products
- About Us
- News
- Support
- Application
- Contact Us
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-29 Origin: Site
This document provides a detailed overview of the soft capsule (softgel) manufacturing process, covering formulation design, raw materials, equipment, and key process steps.
Soft capsules consist of two primary components:
Outer Shell: A flexible, gelatin-based or vegetarian casing that encapsulates the fill material.
Fill Matrix: The active ingredient or formulation contained within the shell, which can be liquid, semisolid, suspension, or emulsion.
The shell provides structural integrity and flexibility. Its key components include:
Source: Derived from partial hydrolysis of collagen from animal tissues (e.g., bones, connective tissues, skin).
Quality Requirements:
Gel strength: 150–200 Bloom
Viscosity: 25–40 mP (centipoise)
Medium particle size
Wide molecular weight distribution

Material: Cassava extract, offering similar functional properties to gelatin for vegetarian capsules.
Role: Solvent for gelatin dissolution.
Proportion: Approximately 45% of the formulation by weight, adjusted based on target viscosity.
Purpose: Enhances flexibility and ductility of the shell.
Common Types: Glycerin, sorbitol.
Ratio: 0.3–1.8, depending on desired shell strength.
Colorants: Natural or synthetic, used for capsule identification, formulated to prevent fading or discoloration.
Opacifiers: Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) to create opacity and protect light-sensitive ingredients.
Preservatives: Extend shelf life.
Flavoring Agents: Vanillin, sucrose, or essential oils to improve taste.
The fill matrix contains the active ingredient and must be designed for stability, bioavailability, and compatibility with the encapsulation process. Common forms include:
Oily Mixtures: Pure oils (e.g., vegetable or fish oils).
Solution Fills: Active ingredients dissolved in non-volatile solvents (e.g., soybean oil, Myglyol 812, diethylene glycol monoethyl ether).
Suspension Fills: Active ingredients dispersed in a carrier, supporting up to 30% solids without compromising flowability.
Design Considerations:
Stability of the active ingredient
Bioavailability
Feasibility of the filling process
Physical stability of the capsule structure
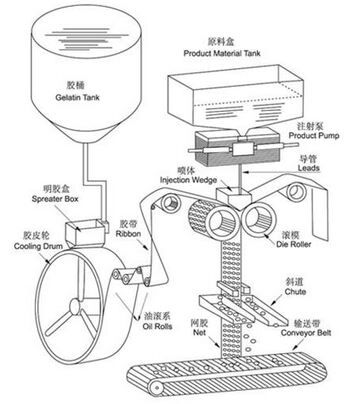
Softgel Encapsulation Machine:
Synchronizes gelatin ribbons.
Delivers and injects the fill matrix between ribbons.
Forms and seals capsules.
Requirements: CE and cGMP compliant, adaptable to various production scales, easy to operate, mold-changeable, highly automated with robust control systems.
Gelatin melting tank
Vacuum homogenizer
Colloid mill
Cooling system drum
Dryer
Drying tray or tunnel polisher
Screening and sorting machine
Pulverizer and recovery machine
Ingredient and liquid storage tanks
Combine gelatin, plasticizer, and water in a heated mixing tank.
Heat for approximately 3 hours until fully melted.
Transfer the gelatin solution to a film-spreading box, maintaining flow.
Form a stable gelatin ribbon using a cooling roller.
Select appropriate equipment (e.g., hammer mill, fluidized bed, mixing tank) based on the fill type.
Ensure uniform mixing and stable properties.
Oil-based mixtures require minimal processing; suspensions or pastes need precise control to maintain consistency.
Transport gelatin ribbons and fill matrix to the tooling system.
Left and right ribbons enter simultaneously.
An air-cooling system regulates temperature and humidity to maintain ribbon condition.
Inject the fill matrix into the mold via a heated injection wedge positioned between die rollers.
Complete molding, sealing, and cutting simultaneously using rollers, with mold design determining capsule size and shape.

Primary Drying: Drum dryer removes ~25% of moisture.
Secondary Drying: Trays in a drying room or tunnel under controlled temperature and humidity for >24 hours.
Use sorting equipment to eliminate defective capsules (e.g., deformed, damaged, or improperly filled).
Inspect for appearance, weight, seal integrity, moisture content, and thickness.
Conduct microbial limit testing as needed.
Apply rotary polishing or solvent cleaning to remove surface residue and enhance capsule appearance and gloss.
Softgel production is a complex, integrated process requiring precise formulation design, high-quality raw materials, advanced equipment, and stringent process control. Proper equipment selection, optimized process parameters, and rigorous quality assurance ensure the production of high-quality soft capsules.